The anterior and posterior belly of the digastric are also involved in the depression of the mandible and elevation of the hyoid bone and are therefore relevant to the masticatory system. Masseter edit edit source Masseter.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub
The sensitivity of the periodontal membrane that surrounds and supports the teeth rather than the power of the muscles of mastication determines the force of the bite.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14112/IjxD1w7xmfmSR4xC7FugCQ_Pterygoideus_lateralis_02.png)
. The cranial nerves contain the sensory and motor nerve fibers that innervate the head. The proximal anterior edge has a pointed process. The medial and lateral pterygoids are located within the fossa itself whilst the masseter and temporalis muscles insert and originate into the borders of the fossa.
The lateral pterygoid muscle is a triangular muscle that lies in the infratemporal fossa. It also carries motor information to the muscles of mastication masseter temporal muscle and the mediallateral pterygoids as well as the tensor tympani tensor veli palatini mylohyoid and digastric muscles. The smaller superior head arises from the inferior surface of the greater wing and infratemporal crest of the sphenoid bone which form the roof of the infratemporal fossa.
The secondary or accessory muscles are. Assess response to light touch over the three sub-divisions of the trigeminal nerve using a piece of cotton wool. Suprahyoid muscles digastric muscle mylohyoid muscle and geniohyoid muscle Infrahyoid muscles the sternohyoid sternothyroid thyrohyoid and omohyoid muscle We will examine the muscles separately.
4 distal lateral to medial. In a baby the. The temporalis masseter medial and lateral pterygoids are the muscles of mastication and these contribute to the elevation depression protrusion and retraction of the mandible.
Like the medial pterygoid muscle the lateral pterygoid has two heads with two distinct origins. The sutural surface with the scapula slopes proximally but is slightly convex Fig. The coracoid foramen is circular.
Facial Expression Muscles Making A Face To Say PSS PSS. Persistent fatigue fevers chills night sweats. Anorexia andor weight loss.
Anterior view of the. The infratemporal fossa forms an important passage for a number of nerves originating in the cranial cavity. 4 proximal lateral to medial.
Mastication masseter temporalis pterygoids Digastric anterior. Movements of the lower jaw in chewing are brought about by the muscles of mastication the masseter the temporal the medial and lateral pterygoids and the buccinator. Belly MYlohyoid tensor Tympani tensor Veli palatine.
By TeachMeSeries Ltd 2022 Fig 2 The medial and lateral pterygoids. In medial and lateral views the blade is almost symmetrical. The coracoid forms more of the glenoid facet than the scapula.
It is a rectangular muscle that. V3 Sensory Branches Buccaneers Are Inferior Linguists. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons lie either in receptor organs eg the nose for smell or the eye for vision or within cranial sensory ganglia which lie along some cranial nerves V VIIX just external to the brain.
Buccal Auriculotemporal Inferior alveolar Lingual. Download high-res image 277KB Download. Aug 01 2020 Odynophagia Otalgia referred from cranial nerve IX via the tympanic nerve of Jacobson Inability to protrude tonguetongue fixationdeep musculature involvement Trismus normal opening from incisor to incisor is 3-4cm medial pterygoid invasion Introduction.

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Wikipedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14112/IjxD1w7xmfmSR4xC7FugCQ_Pterygoideus_lateralis_02.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub

Musclemonday Pterygoid Muscles Today We Are Going To Discuss Our Last Muscle Of The Week The Medial And Lateral Muscle Health And Wellness Physical Therapy
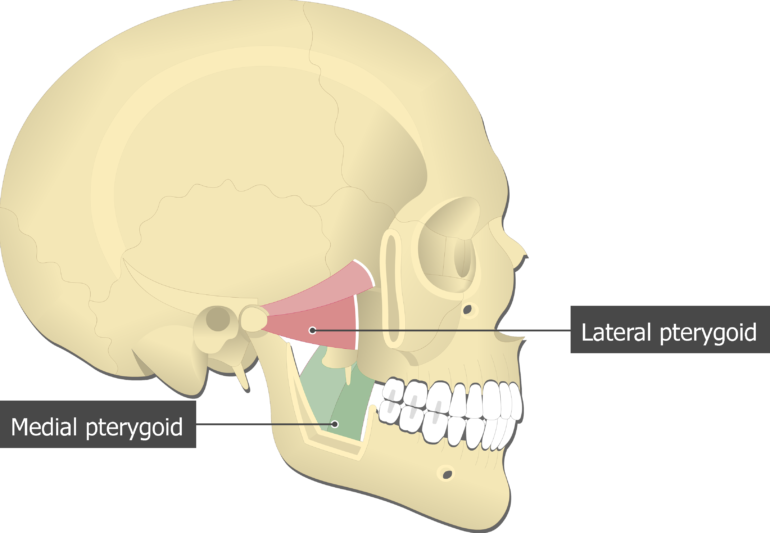
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Attachments Actions Innervation
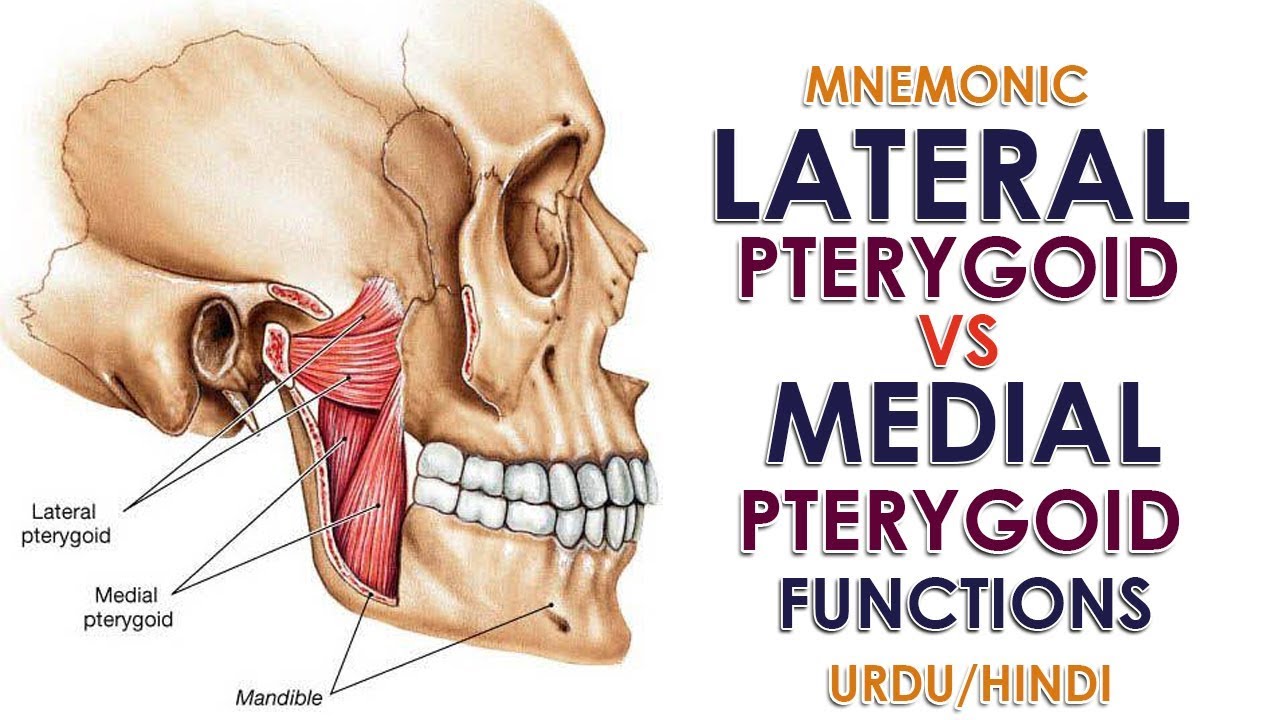
Mnemonic Lateral Pterygoid Vs Medial Pterygoid Function Urdu Hindi Youtube
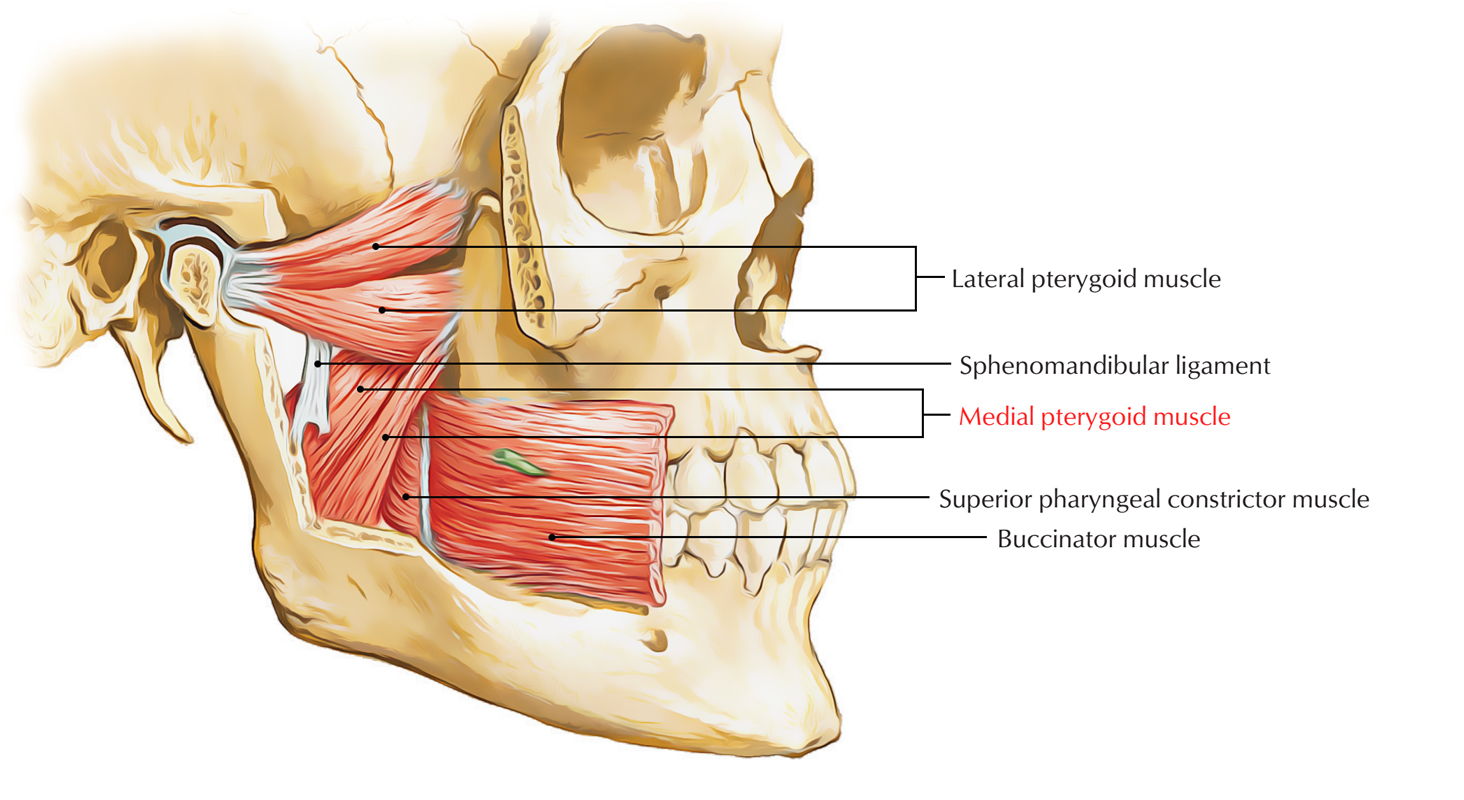
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Earth S Lab
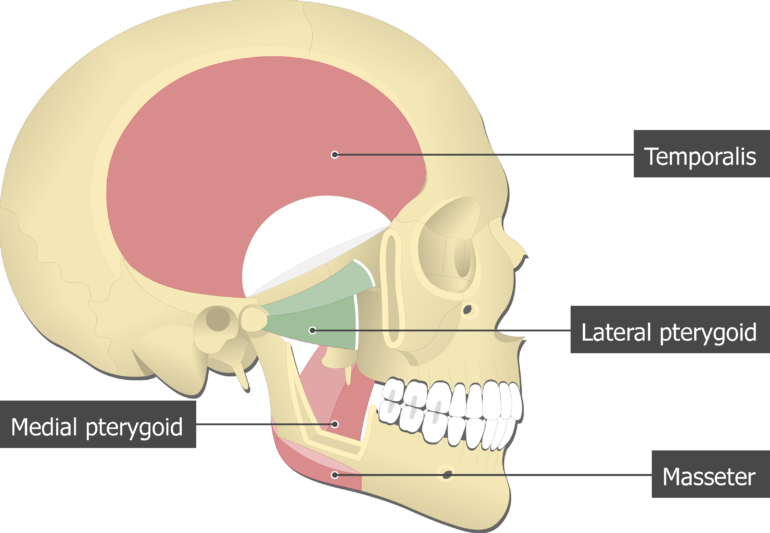

0 comments
Post a Comment